Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from Law Firm Accounts Receivable Management the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. In addition to focusing on these key pillars of top-line growth, we are increasingly considering various other growth avenues, including acquisitions. Genuine Tea is a leading third-wave craft tea Company with an attractive growth and margin profile. This acquisition is the first step in building our platform of next-generation brands.

What Is Gross Income?
Removing the “noise” of administrative or operating costs allows a company to think strategically about product performance and implement cost control strategies more effectively. By also examining operating profit and EBITDA, you can see how well the company’s core business is performing and how much cash it’s generating from its operations. You believe there are going to be tax changes in the future that will be beneficial to the company, or you know that the company is close to gross profit writing off some of its initial startup loans. Even if a company is profitable on paper, it might struggle if there isn’t enough cash on hand to pay the bills. Monitoring cash flow from operations helps ensure the company always remains solvent on a month-to-month basis and can fund its many activities.
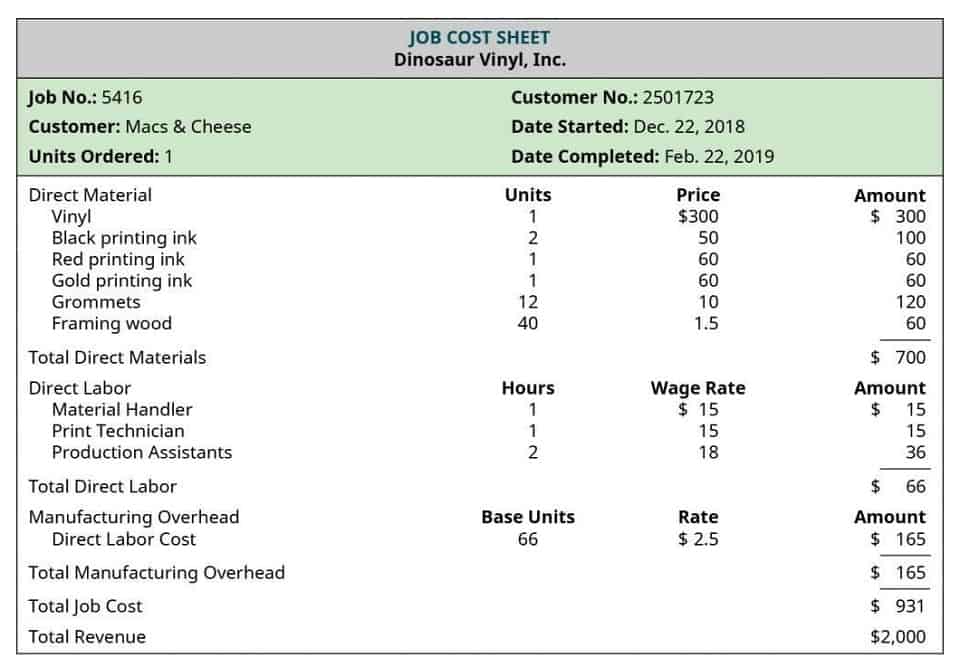
Direct materials and direct labour
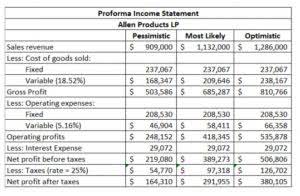
- Therefore, it could be deceiving for the owners and management to analyze their business based on just gross profit.
- For example, a company could be saddled with too much debt, resulting in high interest expenses.
- In addition, in the first quarter of Fiscal 2025, the Company invested more in capital expenditures driven by mandated fire compliance work in the Montreal warehouse.
- You can use it to determine where you should scale up, and where you should cut back.
- The purpose of net income and gross profit are entirely different in terms of determining the success of the company.
- Gross profit is an important metric for assessing a company’s efficiency and productivity.
Net income and net profit are the same single number that represents a specific type of profit. These items are deducted from operating profit before net profit is reached. Non-operating expenses are all the other expenses not part of COGS and operating expenses. Non-operating items are those that are not related to the primary operations of a company. It is recorded as a business expense on an income statement since COGS is the cost of doing business. Below we will discuss gross profit and net profit, explore their formulas, and highlight some key differences between the two.

Gross Profit Ratio: Definition
The higher the gross profit, the greater the efficiency of management in relation to production/purchasing and pricing. Expenses here can include COGS, operating expenses, loan interest, taxes, and any other costs. For example, if Company A has $100,000 in sales and a COGS of $60,000, it means the gross profit is $40,000, or $100,000 minus $60,000.

Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed normal balance resources. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.